Double Fork Hydraulic,Hydraulic Adjustable Fork,Adjustable Forklift Forks Hydraulic,Industry Mechanical Adjustable Fork Shandong Techence Forging Co.,Ltd , https://www.shandongtechence.com

Shanghai Optoelectronics has made new progress in the measurement of high-altitude sodium layer magnetic field
[ Instrument Network Instrument Development ] Recently, Zhou Tianhua and Feng Yan project team of Shanghai Laser Institute's Space Laser Information Technology Research Center made progress in the study of high-altitude sodium layer magnetic field measurement, using self-developed high-power yellow laser, based on gated photons. For the first time, the counting technology remotely measured the magnetic field of the high-altitude sodium layer (85-100 km). This technology has applied for a patent for invention (publication number: CN110161433A), and related research results are published in [Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 124, 7505-7512 (2019)].
Experimental device schematic and transmitting telescope
Remote measurement of the geomagnetic field in the middle layer will provide a powerful tool for mapping the Earth's lithospheric magnetic field, monitoring the magnetic perturbations associated with aurora, and performing long-term continuous measurements of ionospheric currents in the polar regions. At present, the reported intermediate layer magnetic field measurements are based on phase sensitive detection techniques. However, when the echo photon rate is too low, the filtering cannot give a continuous signal, and the phase sensitive detection technique is difficult to use. The advantage of gated photon counting technology is that it is still applicable under the condition that the number of echo photons is extremely small. At the same time, it has unique advantages in background light suppression, which can effectively suppress other sources (Rayleigh scattering, rice scattering and Laser) interference; and the ability to collect fluorescence from a specific height of the sodium layer for potential applications in achieving highly reproducible magnetic field measurements.
Gated photon counting schematic
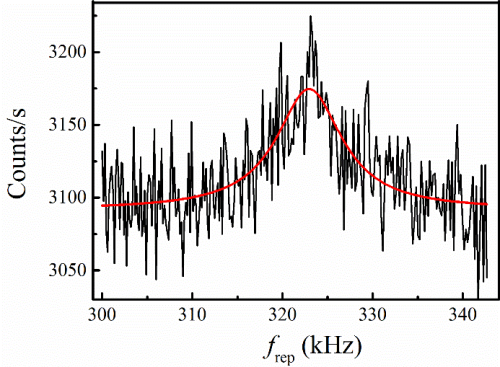
Based on the gated photon counting and direct pulse repetition frequency scanning, the project team designed a high-altitude magnetic field measurement scheme by using the spin precession of the middle layer sodium atom in the magnetic field. This technique uses an intensity modulated laser beam to optically pump the sodium in the middle layer, scans the pulse repetition frequency, and collects the fluorescence echo using a ground-based large aperture telescope to infer the magnetic field. The field test was strongly supported by the Chengdu Institute of Optoelectronics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The magneto-optical resonance curve of the stable intermediate layer sodium atom was first detected on the 1.8 m caliber telescope at the Lijiang Astronomical Observatory of the Yunnan Astronomical Observatory. The technology was successfully verified.
Measured typical magneto-optical resonance signal